# Media
The media field is an adaption for a core WordPress feature.
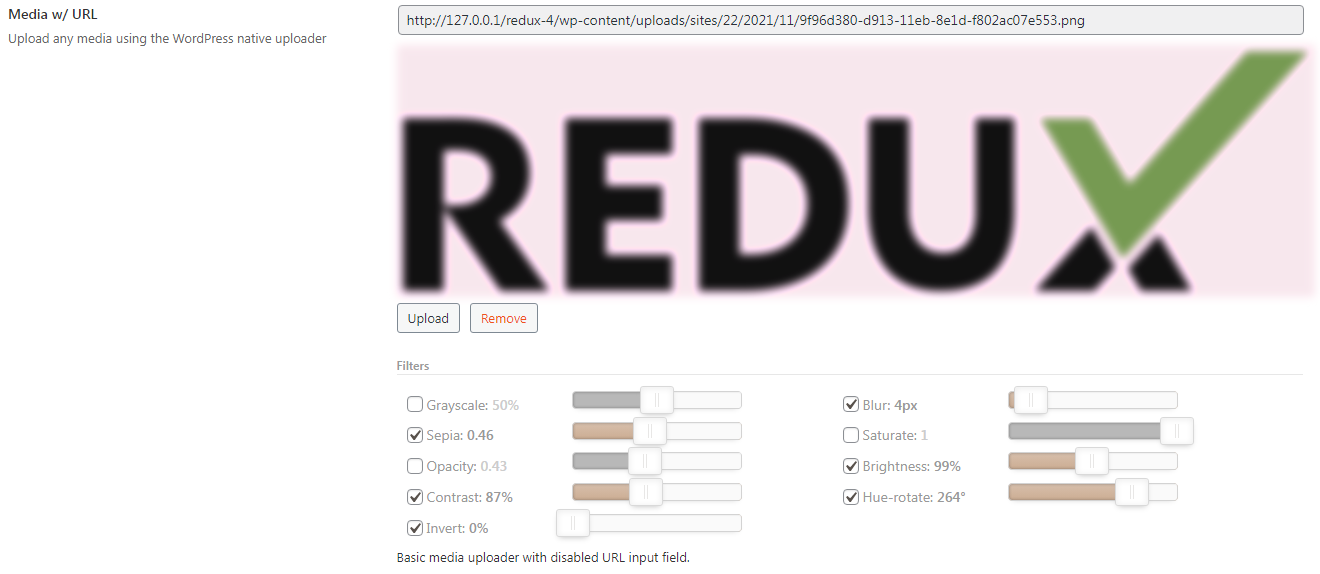
Table of Contents
# Arguments
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| type | string | media | Value identifying the field type. |
| width | string | Sets the width of the image. | |
| height | string | Sets the height of the image. | |
| url | bool | true | Flag to display the image of the URL. |
| alt | string | The alt test of the image. | |
| preview | bool | true | Flag to display a preview of the image. |
| preview_size | string | thumbnail | Set the size of the preview image. |
| placeholder | string | No media selected | Sets the text that appears in the URL input box when no value is present. |
| readonly | bool | true | Flag to set the readonly attribute of the media text field. |
| mode | string | image | String specifying either the file type or mime type of files to accept from the media library. IE, the file selector will not let you add any other types. |
| class | string | Additional classe name add to the field. | |
| library_filter | array | Accepts an array of strings which correspond to the second part of a mime type (opens new window) (i.e. video/mp4 would be “mp4”). Only files that match one of the items in the array will appear in the media library. | |
| filter | array | Array of filter sliders to display to the user. See Image Filters below. |
Also See
# Image Filters
While it's possible to use the values returned to the global options variable to set your CSS manually, we've included the option to automatically our your filter's values automatically. To use this, you'll need to set the class name of the target image in the output argument as noted in the example below.
| Filter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| grayscale | false | Slider to adjust the image grayscale. |
| blur | false | Slider to adjust the image grayscale. |
| sepia | false | Slider to adjust the image blur. |
| saturate | false | Slider to adjust the image saturation. |
| opacity | false | Slider to adjust the image opacity. |
| brightness | false | Slider to adjust the image bightness. |
| contrast | false | Slider to adjust the image contrast. |
| hue-rotate | false | Slider to adjust the image hue rotation. |
| invert | false | Slider to adjust the image inversion. |
# Default Options
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | string | Unique ID for the media type. |
| url | string | Full URL to the default media. |
| width | string | Sets the width of the media. |
| height | string | Sets the height of the media. |
| thumbnail | string | URL to the media thumbnail, if any. |
| filter | array | Array of individual filter settings used to set checked state and default value. See Image Filter Defaults below. |
# Image Filter Defaults
Each filter's settings are set via an array of two individual settings: checked and value. The checked setting determines the default state of the slider, whether it is enabled or disabled. The value setting sets the default position of the filter's slider.
| Filter | Values |
|---|---|
| grayscale | 'checked' => false'value' => 0 |
| blur | 'checked' => false'value' => 0 |
| sepia | 'checked' => false'value' => 0 |
| saturate | 'checked' => false'value' => 1 |
| opacity | 'checked' => false'value' => 1 |
| brightness | 'checked' => false'value' => 100 |
| contrast | 'checked' => false'value' => 100 |
| hue-rotate | 'checked' => false'value' => 0 |
| invert | 'checked' => false'value' => 0 |
# Build Config
Redux::set_field( 'OPT_NAME', 'SECTION_ID', array(
'type' => 'media'
) );# Example Config
Redux::set_field(
'OPT_NAME',
'SECTION_ID',
array(
'id' => 'opt-media',
'type' => 'media',
'url' => true,
'title' => esc_html__('Media w/ URL', 'your-textdomain-here'),
'desc' => esc_html__('Basic media uploader with disabled URL input field.', 'your-textdomain-here'),
'subtitle' => esc_html__('Upload any media using the WordPress native uploader', 'your-textdomain-here'),
'default' => array(
'url'=>'https://s.wordpress.org/style/images/codeispoetry.png'
),
)
);
# Example Config w/ library_filter and filters
This example will produce a media field that can only find files with the extension denoted. This is useful when you only want specific file types specified for a given field.
Redux::set_field(
'OPT_NAME',
'SECTION_ID',
array(
'id' => 'opt-media',
'type' => 'media',
'title' => esc_html__('Media w/ Library Filter', 'your-textdomain-here'),
'library_filter' => array(
'jpg'
),
'filter' => array(
'blur' => true,
'opacity' => true,
),
'default' => array(
'blur' => array(
'checked' => true,
'value' => 0,
),
'opacity' => array(
'checked' => true,
'value' => 0,
)
),
'output' => array('.your-image-class'),
)
);
# Example Usage
This example is based on the example usage provided above. Be sure to change $redux_demo to the value you specified in your opt_name argument.
global $redux_demo;
echo 'URL value: ' . $redux_demo['opt-media']['url'];
echo 'Height value: ' . $redux_demo['opt-media']['height'];
echo 'Width value: ' . $redux_demo['opt-media']['width'];
echo 'Thumbnail value: ' . $redux_demo['opt-media']['thumbnail'];
# Allowed File Types in WordPress
WordPress allows you to upload many of the most common image files, audio/video, PDF, Microsoft Office and OpenOffice documents. The WordPress codex has a full list of allowed file types (opens new window) and extensions.
To find out which mime types are enabled in your instance, you can run the following code:
print_r( get_allowed_mime_types() );
# Adding Additional File Types
Security is the main reason behind the limitation on file types that users can upload. You can, however, get around this with a bit of code. Add this code to your theme or plugin to allow SVG files to be uploaded:
function my_mime_types( $mime_types = array() ){
$mime_types['svg'] = 'image/svg+xml'; // Adding svg extension
return $mime_types;
}
add_filter('upload_mimes', 'my_mime_types', 1, 1);
Notice that the file extension goes as the key in $mime_types associated array and the mime type goes as its value. In
this example, SVG file extension represents files with the mime type image/svg+xml. You can find out mime types of
several common file extensions on this page (opens new window).
You can also add multiple file types in one code snippet, like this:
function my_mime_types( $mime_types = array() ){
$mime_types['svg'] = 'image/svg+xml'; // Adding svg extension
$mime_types['psd'] = 'image/vnd.adobe.photoshop'; // Adding photoshop files
return $mime_types;
}
add_filter('upload_mimes', 'my_mime_types', 1, 1);
← Link Color Multi Text →